The Gorai River
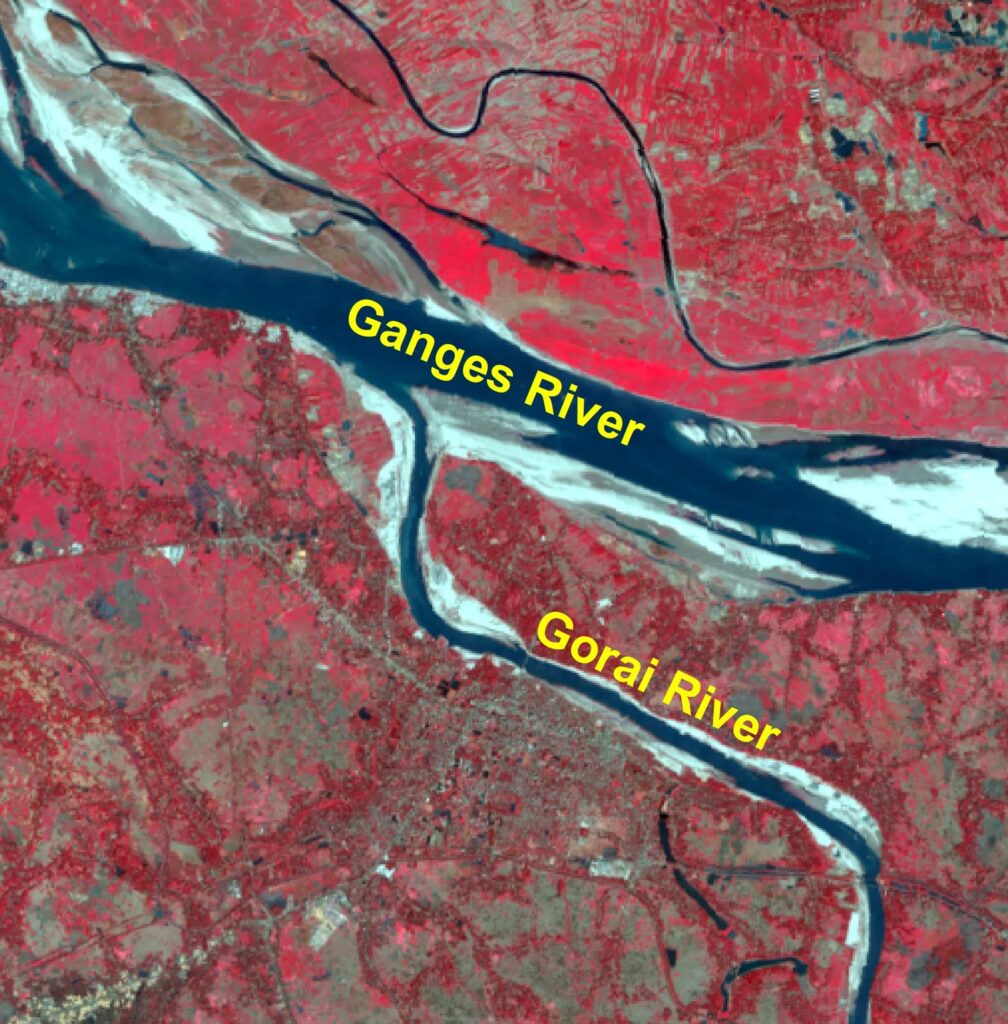
The Gorai is a key river in Bangladesh. It originates from the Ganges River. It is the main source of the freshwater flow to the S-W part. The river links with the Madhumati R that meets the Nabaganga R. Then, the Nabaganga joins with the Rupsa-Pasur system. Afterwards, it drains to the sea. So, the ecosystem of Sundarbans is guided by this river.
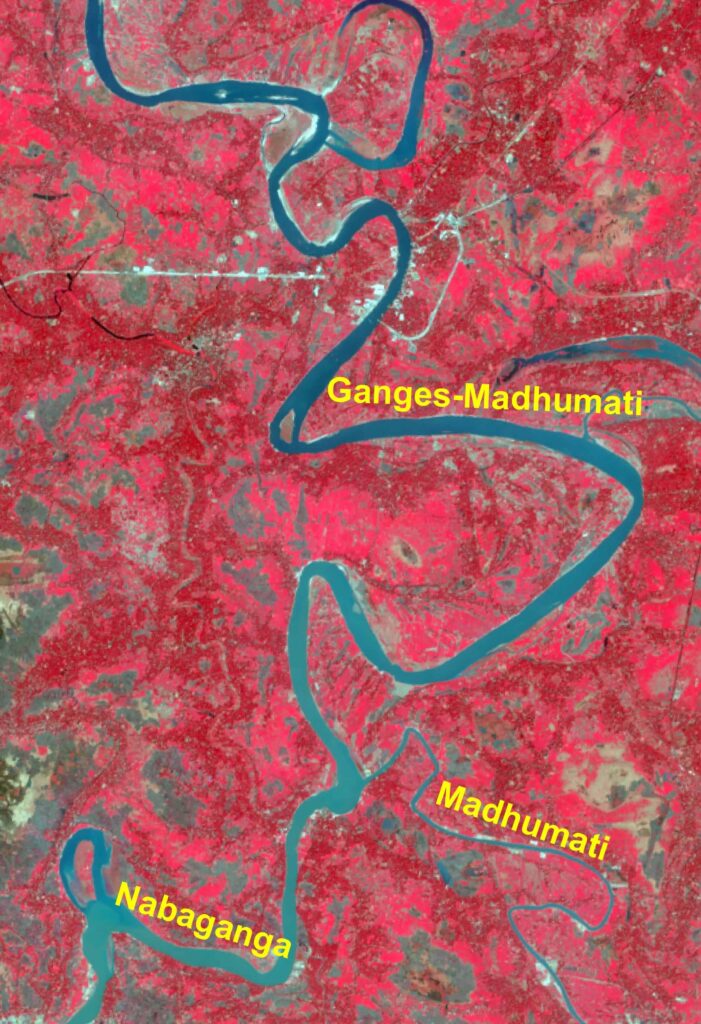
Gorai-Madhumati-Nabaganga System 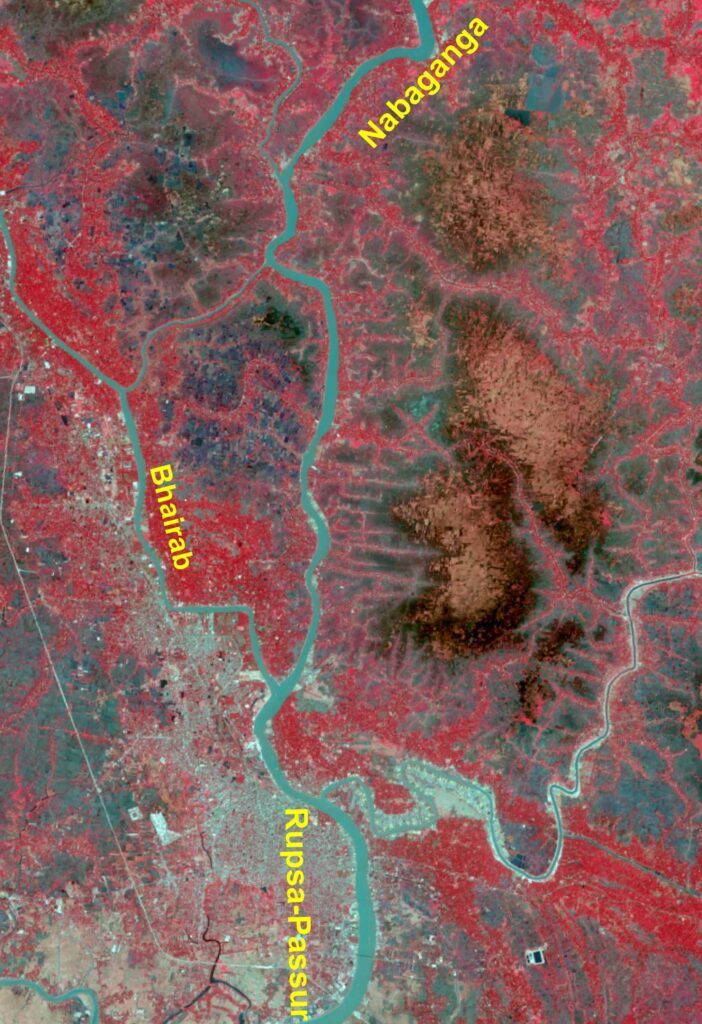
Nabaganga-Rupsa-Passur System
Key Features
Besides, the length of the river is 87 km. The mean width is 300 m. The flow is high in monsoon and less in lean period. Tides has no effect. River is more dynamic at the downstream.
Value of the Gorai River
- Pushes salinity level to the sea;
- Maintains healthy ecosystem in the system;
- People depends on the Gorai flow;
- Maintains navigation to carry goods and people;
- Crop production is dependent on the Gorai flow.
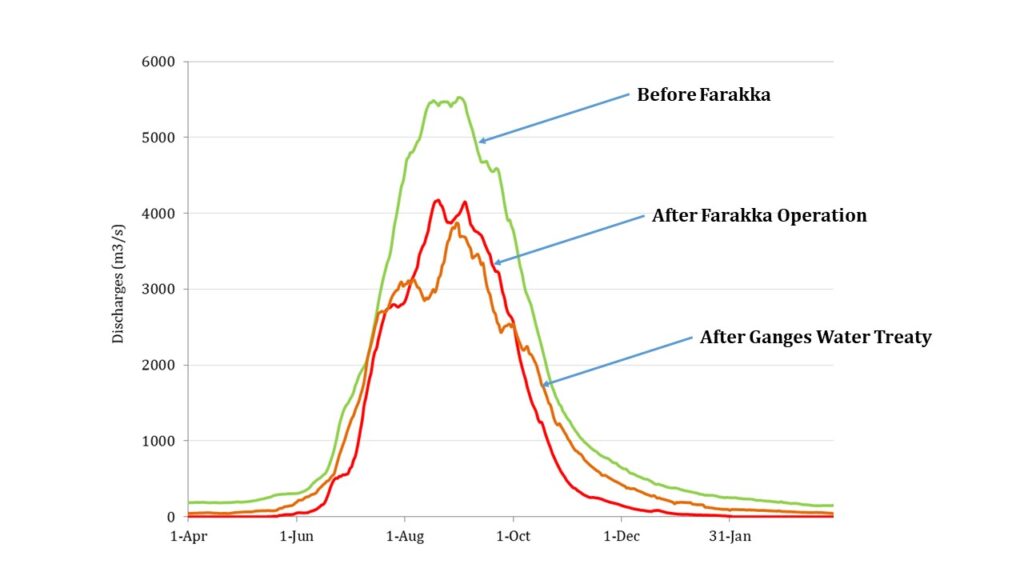
Flow in the dry season of the Gorai R is largely related to the flow of the Ganges R. Besides, the mouth of the Gorai is often closed. Sand often enters the system from the Ganges R. Moreover, Farakka Barrage plays an important role in keeping the flow in the Gorai R. But, the dry season flow in the Gorai has hugely reduced after the operation of the Farakka barrage in 1975. Also, It became even zero at Gorai Rly. Bridge. Ganges Water Treaty in 1996 helps to improve the flow. In addition to that, dredging may ensure flow.
Expert Opinions:
The management of the mouth of the Gorai R is needed. River Training Works at the Gorai mouth as well as dredging could certainly ensure flow to the river. In addition to that, construction of the Ganges Barrage would provide solution of flow in Ganges Dependent area that covers Gorai River.
